Previous
Part 4: Test locally
Part 5 of 5 | ⏱️ 20-25 minutes | Advanced
Complete Parts 1-4 first. You should have a working single-model module before adding more models.
GetReadings methodSome of the code you generated for your first modular resource is shared across the module no matter how many modular resource models it supports. Some of the code is resource-specific.
If you have multiple modular resources that are related, you can put them all into the same module.
Use multiple models when:
Use separate modules when:
Our example hardware:
Since the Camera API can’t return numbers and the Sensor API can’t return images, we need two models.
For convenience, run the module generator again from within your existing module’s directory to generate code for the sensor:
Change directory into your module:
cd hello-world
Run the generator for the sensor model:
viam module generate --language python --model-name hello-sensor \
--name hello-world --resource-subtype=sensor --public false \
--enable-cloud true
When prompted whether to register the module, select No. Your module is already registered.
viam module generate --language go --model-name hello-sensor \
--name hello-world --resource-subtype=sensor --public false \
--enable-cloud true
When prompted whether to register the module, select No. Your module is already registered.
This creates a temporary nested hello-world/hello-world/ directory. You’ll copy the sensor-specific code from it.
Now integrate the sensor model into your existing module:
Move the generated sensor model file:
mv hello-world/src/models/hello_sensor.py src/models/
Open src/main.py and add HelloSensor to the imports:
import asyncio
from viam.module.module import Module
try:
from models.hello_camera import HelloCamera
from models.hello_sensor import HelloSensor
except ModuleNotFoundError: # when running as local module with run.sh
from .models.hello_camera import HelloCamera
from .models.hello_sensor import HelloSensor
if __name__ == '__main__':
asyncio.run(Module.run_from_registry())
Save the file.
Move the sensor documentation file:
mv hello-world/<org-id>_hello-world_hello-sensor.md ./
Open meta.json and update the description to mention both models:
{
"$schema": "https://dl.viam.dev/module.schema.json",
"module_id": "exampleorg:hello-world",
"visibility": "private",
"url": "",
"description": "Example camera and sensor components: hello-camera and hello-sensor",
"applications": null,
"markdown_link": "README.md",
"entrypoint": "./run.sh",
"first_run": "",
"build": {
"build": "./build.sh",
"setup": "./setup.sh",
"path": "dist/archive.tar.gz",
"arch": ["linux/amd64", "linux/arm64", "darwin/arm64", "windows/amd64"]
}
}
Save the file.
Delete the temporary directory:
rm -rf hello-world/
Rename module.go to hello-camera.go:
mv module.go hello-camera.go
Move and rename the sensor model file:
mv hello-world/module.go hello-sensor.go
Open cmd/module/main.go and register both models:
package main
import (
"helloworld"
"go.viam.com/rdk/module"
"go.viam.com/rdk/resource"
camera "go.viam.com/rdk/components/camera"
sensor "go.viam.com/rdk/components/sensor"
)
func main() {
// ModularMain can take multiple APIModel arguments, if your module implements multiple models.
module.ModularMain(
resource.APIModel{ camera.API, helloworld.HelloCamera},
resource.APIModel{ sensor.API, helloworld.HelloSensor},
)
}
Save the file.
Move the sensor documentation file:
mv hello-world/<org-id>_hello-world_hello-sensor.md ./
Open meta.json and update the description to mention both models:
{
"$schema": "https://dl.viam.dev/module.schema.json",
"module_id": "exampleorg:hello-world",
"visibility": "private",
"url": "",
"description": "Example camera and sensor components: hello-camera and hello-sensor",
"applications": null,
"markdown_link": "README.md",
"entrypoint": "bin/hello-world",
"first_run": "",
"build": {
"build": "make module.tar.gz",
"setup": "make setup",
"path": "module.tar.gz",
"arch": ["linux/amd64", "linux/arm64", "darwin/arm64", "windows/amd64"]
}
}
Save the file.
Since errUnimplemented and Config are already defined in hello-camera.go, update hello-sensor.go:
"errors" import (if it exists only for errUnimplemented)errUnimplemented = errors.New("unimplemented")type Config struct { to type sensorConfig struct {*Config in hello-sensor.go with *sensorConfigDelete the temporary directory:
rm -rf hello-world/
✅ Checkpoint 1: Sensor code integrated
Now implement the GetReadings method for the sensor:
Open src/models/hello_sensor.py and find the get_readings method (around line 63).
Replace raise NotImplementedError() with:
async def get_readings(
self,
*,
extra: Optional[Mapping[str, Any]] = None,
timeout: Optional[float] = None,
**kwargs
) -> Mapping[str, SensorReading]:
number = random.random()
return {
"random_number": number
}
Add the import at the top of the file:
import random
Save the file.
Code explanation:
Open hello-sensor.go and find the Readings method (around line 92).
Replace panic("not implemented") with:
func (s *helloWorldHelloSensor) Readings(ctx context.Context, extra map[string]interface{}) (map[string]interface{}, error) {
number := rand.Float64()
return map[string]interface{}{
"random_number": number,
}, nil
}
Add the import at the top of the file:
"math/rand"
Save the file.
Code explanation:
Note that the sensor has no configurable attributes, so you don’t need to modify the validation or reconfiguration methods.
✅ Checkpoint 2: Sensor implementation complete
Now test your multi-model module:
Reload the module using hot reload:
viam module reload --part-id YOUR_PART_ID
Add the sensor component:
exampleorg:hello-world:hello-sensorsensor-1Test the sensor:
{"random_number": 0.xxxxx} with a random numberVerify camera still works:
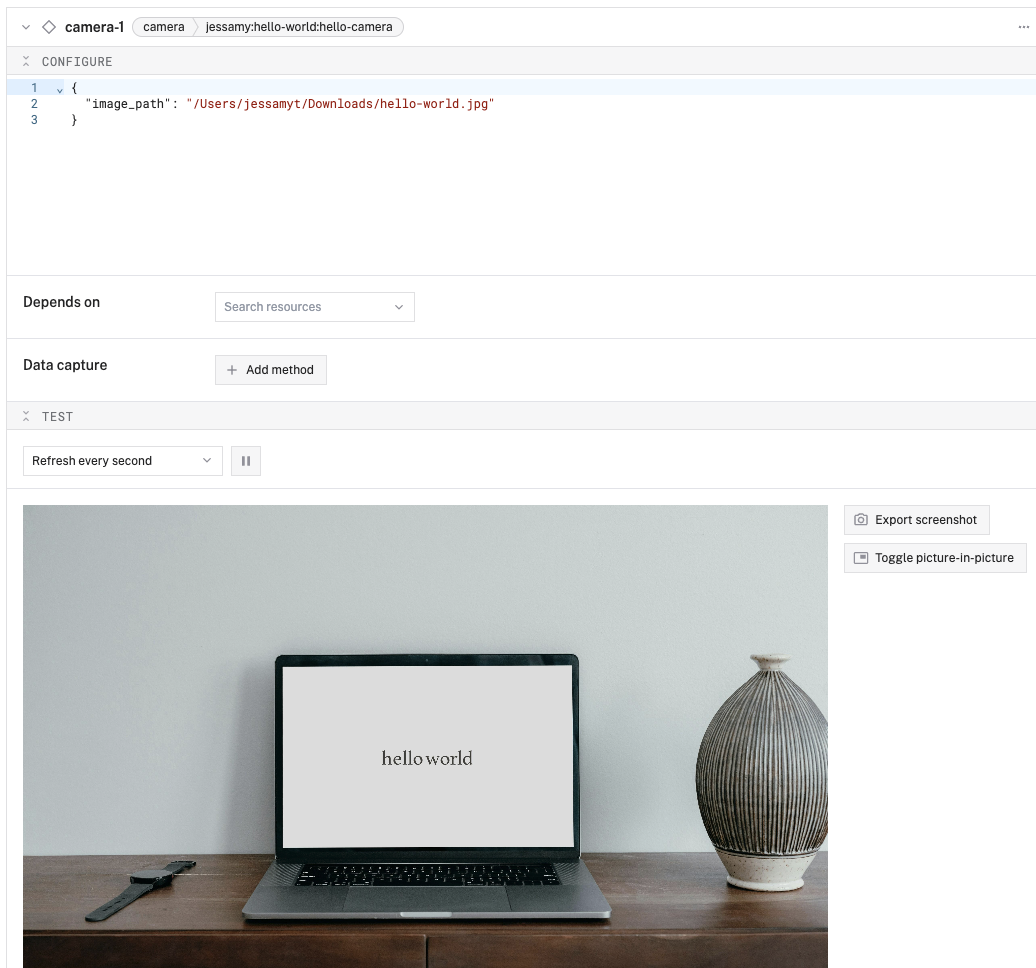
✅ Checkpoint 3: Both models working!
For modules with many models, consider this structure:
my-module/
├── src/
│ ├── models/
│ │ ├── model1.py
│ │ ├── model2.py
│ │ └── model3.py
│ ├── utils/
│ │ └── shared.py
│ └── main.py
✅ Multi-model module created:
✅ Complete implementation:
✅ Understanding:
Congratulations! You’ve created a complete, working module with multiple models. Now you’re ready to:
Tutorial navigation:
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! If you have any other feedback please let us know:
We're sorry about that. To help us improve, please tell us what we can do better:
Thank you!